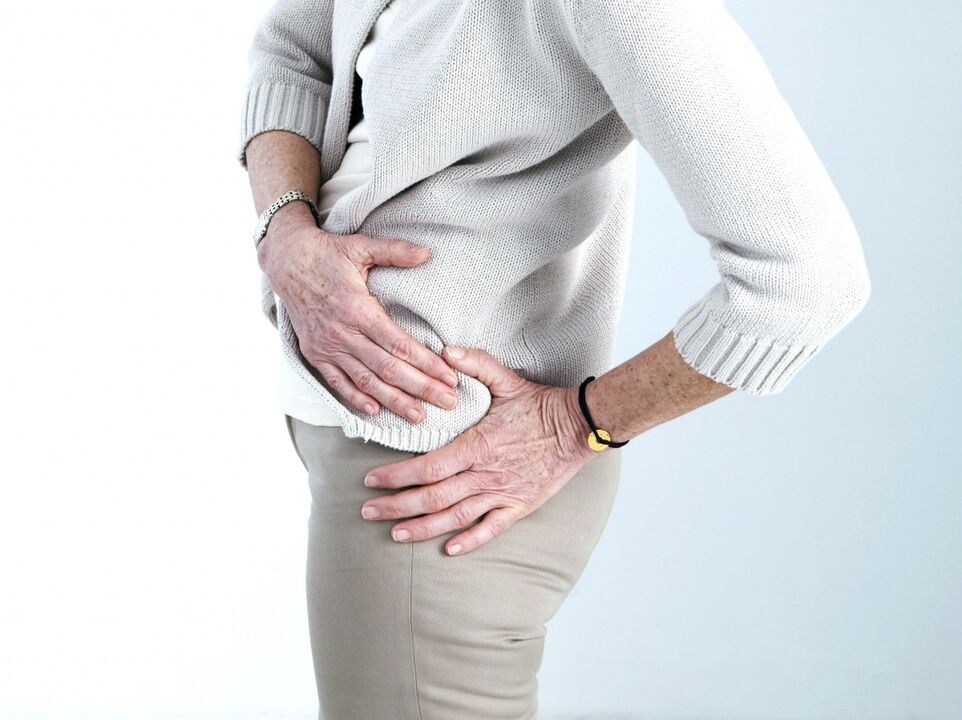
The presence of hip pain should definitely be a cause for alarm, as this is the largest bone connection and without it the process of walking would be impossible. It maintains balance and redistributes weight between the spine and lower extremities. When hip function is compromised, the patient's quality of life decreases immediately and physical activity decreases.
If you experience hip pain, you need to determine the cause. Pain management depends on the pathology it is a symptom of. Complicated measures and strict adherence to the recommendations will help to get rid of the disease and maintain the motor activity of the joints.
The destruction of the hip joint makes it impossible to move actively. Decreased function can limit the patient's independent movement and performance.
So what causes this unpleasant discomfort in the hip joint, and how can it be treated at home? Let's try to figure it out.
reason
Hip pain can occur for a variety of reasons: due to damage to the joint itself, whether on the right or left side, and the bones, cartilage, or ligaments that lie next to it. Numbness and limited movement of the entire hip is often accompanied by painful symptoms.
Hip disease can appear at any age, but it is most common in the elderly. If pain occurs, it is advisable to consult a GP who will prescribe an initial examination and recommend which doctor you should see.
The most common causes of hip pain are:
- dislocation;
- fracture;
- Infectious inflammation or arthritis;
- degenerative changes or osteoarthritis (hip disease);
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head;
- Inflammation of the pockets around the joints (bursitis);
- Non-infectious inflammation in connective tissue autoimmune diseases;
- pregnancy period.
The prevalence of pain syndromes in this localization increases with age. If hip pain occurs in 8-10% of young adults under the age of 18, for middle-aged adults, the figure is 20-30%. At the age of 50-59, 40% of people already have the disease, and in the elderly - from 50% to 60%. Women are more likely than men to suffer from this positioning pain syndrome.
According to age
Typical pathological conditions in different age groups cause hip pain:
- adults and seniors. Osteoarthritis (arthropathy of the hip), joint damage and deformity, compression of the acetabulum.
- Children and teenagers. Perthes disease, transient synovitis, acquired varus deformity, tuberculous lesions, joint damage and deformity.
- Newborns and infants under 1 year old. Congenital hip dislocation, epiphyseal consequences in general, acute suppurative osteoarthritis, congenital varus deformity.
Bursitis
The main symptoms of bursitis:
- With the development of the disease, back pain occurs;
- Increased discomfort when moving the leg;
- Increased pain after prolonged sitting, back pain;
- Severe and burning pain, especially when lying on your side at night, that extends over the entire surface of the thigh.
If an infection enters, purulent bursitis may develop, which is characterized by acute pain in the hip joint. A characteristic symptom of this type of bursitis is the inability to fully extend the leg. As you press, you feel a firmness that spreads over the large surface of your thighs. Maybe it's back pain.
Osteoarthritis (Hip Disease)
Hip disease is based on a process of degeneration (destruction) and malnutrition (malnutrition) of the hip joint. As a result, the joint stops performing its function - the movement of the leg is disrupted. It can be an independent disease or secondary joint damage (bone tumor). In old age, hip joint disease can recur after a hip fracture.
There are 3 stages of hip arthropathy depending on the severity of changes in the joint.
- In stage 3, hip pain can be bothering the patient even when resting at night. Significant limp, forcing the use of crutches.
- In stage 2 of hip arthropathy, pain begins to radiate into the groin, inner thigh, and front, usually down to the knee. They appear after the usual daily load, but they don't bother when resting.
- Stage 1 is characterized by hip pain when overworked: climbing stairs with heavy objects in hand, walking more than 2-3 km, running. The pain will subside after a short rest.
The choice of treatment for hip arthropathy depends on the severity of the changes in the joint. Grade 1 and 2 disease can usually be managed conservatively. Anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotective agents, drugs to improve blood circulation to the joints, physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises are prescribed. The final stage is processed only with the help of operations.
hip fracture
A very common injury, especially in older adults with weaker bones. This condition is characterized by severe pain and the inability to perform any movement in the joint.
In this case, hospitalization is necessary for proper treatment, as hip fractures are often complicated by infectious processes, such as bacterial arthritis. Increased inflammation can significantly impair fracture healing and lead to incorrect bone fusion.
hip dislocation
Mostly it is the result of road accidents and also occurs during falls and various occupational injuries.
Clinical manifestations of dislocation: unbearable acute pain, almost absolute difficulty in lower extremity movement, with nerve ending damage, loss of sensitivity of the ankle joint. In bilateral joint dislocations, the symptoms are intermittent lameness or the so-called "duck gait".
It is worth emphasizing the concept of congenital hip dislocation diagnosed in neonates. This disease is caused by underdevelopment of the acetabulum, which causes the femoral head to move away from its limits, creating a dislocation.
subluxation
This is an incomplete loss of contact between the femoral head and the acetabulum. The person does not experience severe pain, and motor activities are slightly limited, but unpleasant sensations persist.
Rheumatism
Systemic disease of connective tissue with damage to joints and heart valve organs. Girls and young women are more likely to develop this after strep throat.
About two weeks after the onset, severe pain in the large joints appeared, and the pain gradually decreased and disappeared. Rheumatism does not cause permanent damage to the joints, and its main risk is the development of acquired heart defects.
arthritis
Arthritis is especially common in older adults. The older a person is, the more processes take place within the joints. Discomfort in the legs and groin area, cramps can be felt in the front of the thighs, even up to the knees. Symptoms are worse when walking and resting on the legs. Getting up from a sitting position becomes difficult, which can cause severe pain in the hip joint.
Most of the time, discomfort increases in the morning, but it decreases with physical activity. But as the load becomes too great, the unpleasant sensations increase and motion stiffness develops. Treatment depends on the diagnosis and is usually prescribed with anti-inflammatory drugs, exercise therapy, and hormonal medications.
Infect
Infectious arthritis can be caused by viruses such as influenza, staphylococcus, streptococcus… In this case, the disease can progress rapidly. Fever begins and swelling is observed in the affected joint area. Acute pain in the hip joint is observed with movement or even touching the affected area.
Slightly different symptoms are observed in tuberculous arthritis, which most commonly affects the hip joint. In this case, the disease gradually makes itself felt. At first, a person begins to experience mild soreness while walking that radiates to the leg - the middle part of the thigh or knee. As the disease progresses, hip movement is restricted in all directions, and the affected area swells.
tendonitis
Tendon inflammation, or tendonitis, often affects people who regularly engage in high-level physical activity. Mostly, these are athletes. It should be noted that this disease sometimes progresses unknowingly, especially if the patient relieves the load on the hip joint. Conversely, if the movement is too active and overloaded, the pain can become very intense.
Tendonitis is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
Which doctor is treating?
If you have hip pain, you may need help from these doctors:
- rheumatologist;
- Traumatologist or orthopedic surgeon;
- physical therapist;
- neurologist.
The specialist will investigate and examine the patient for a comprehensive examination.
diagnosis
Laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- X-rays and ultrasounds. They are the gold standard for nearly all hip disorders.
- General blood analysis. It will provide an opportunity to assess the general condition of the body.
- Biochemical blood tests and specific markers for rheumatism.
- Urine test. Determination of urine color, quantity, transparency and density. In addition, protein, glucose and bilirubin are also important indicators.
- Morphological examination of biopsy specimens. It is used to study the structure of the extracted material, especially in the case of suspected bone tumor disease.
- CT scan. Allows visualization of joint, bone tissue in several projections to determine its density.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Presents thin layers of body tissue on any plane.
- Bone imaging. With the introduction of bone radiopharmaceuticals, the state of blood flow and the intensity of metabolic processes in bone tissue were visualized.
Note the decrease in joint range of motion. Remember whether the disease is accompanied by local manifestations such as fever, headache, local congestion, and edema. Don't be afraid to call the attention of experts to the possible cause of the disease. Describe in detail everything that is bothering you.
How is hip pain treated?
What should I do if I notice pain symptoms in the hip area? After all, the pelvis is an important link in the musculoskeletal system. If there is severe pain, you should contact a specialist immediately. He will help diagnose and determine the cause of the problem. The earlier a diagnosis is made, the more effective the treatment will be.
If mild pain is suspected to be related to a minor injury or joint overload, the following can be done:
- Avoid putting pressure on sore joints and keep calm;
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- When sleeping, it is recommended to lie on your side to be healthy.
Medication includes complex drug intake in all directions:
- Hondoprotectors, mineral and vitamin complex.
- Muscle relaxants that reduce spasms caused by pain.
- NSAIDs and steroids. Steroid medicines are only used for severe symptoms.
- Means of improving microcirculation. They relieve edema and hypoxic manifestations in the affected area.
- Diuretics reduce swelling in inflamed areas.
Physical therapy measures are also important in the management of hip disorders. They are performed after the resolution of acute inflammation and severe pain. Electrophoresis has proven itself well, with the help of which it is possible to generate high concentrations of drugs directly in the affected area.
A progressive approach is considered laser therapy, which produces analgesic, absorbing and anti-inflammatory effects. Magnetic therapy, diode dynamic therapy, and drug sonication therapy have also been used successfully.