Compared with the cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis found in every 2-3 patients 18 years and older, it is almost impossible to diagnose thoracic osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine (GO). This phenomenon can be explained by the special structure of the thoracic spine-there are a large number of intervertebral discs, and the intervertebral discs have a finer structure. This part of the spine has low mobility, so the load it bears is not high, because the main "strike" is shared by the sternum and ribs.
The main reason for the development of thoracic lesions is the increased load on the intervertebral discs, thus destroying the metabolic process and its structure. . . In the presence of this disease, the shock absorption performance of the intervertebral disc is lost, and the annulus fibrosis becomes thinner and dry. After this process, the nerve endings become inflamed, people will feel continuous pain, discomfort, and reduced motor activity. As the disease progressesWith rapid development, it will affect the spine and joint ligaments.
Now, many experts have classified osteochondrosis as routine, not according to the stage of the disease course, but according to the degree, and also according to the specificity of the symptoms.
If we consider the general symptoms, then osteochondrosis in the sternum is not as obvious as other types, but there is a typical clinical manifestation. Therefore, patients may complain of the following signs:
- Pain in the chest area, usually aggravated by prolonged exposure to one location or at night;
- Pain between the shoulder blades, which increases with raising the arm or physical exertion;
- Feeling discomfort and pain when trying to breathe deeply, and this symptom also occurs when you exhale;
- When walking, the ribs are sore and the chest feels squeezed.
This performance can be accompanied by a number of weeks, which should be regarded as a deterioration of the disease.
What other symptoms can be observed with H2O? In addition to the main clinical manifestations, the following manifestations may also occur in some cases:
- Numbness in the upper limbs, and the skin has the sensation of "goose bumps";
- Destruction of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Feeling cold in the legs, unable to warm them.
In addition, the characteristic sign of this disease is back pain-severe pain between the shoulder blade and back pain-a slow pain syndrome with no obvious picture.
It should be noted that, like any other type of osteochondrosis, chest disease usually affects people with inactive lifestyles. Often sitting in front of the computer, bending over, and heavy physical exertion have also become incentives for the development of the disease.
How this disease manifests in women and men
The development of the process of degenerative dystrophy in the chest area of the patient is considered to be a diagnosis-thoracic osteochondrosis. This disease can cause destruction of the intervertebral disc and malnutrition of the connective tissue structure. In addition, the blood circulation process is disturbed due to the inactivity of the chest area. And the pain syndrome itself occurs due to the squeezing of nerve endings in the course of pathological progress.
As statistics show, women suffer from HO more than men and are younger. The main reason for this phenomenon is the change in hormone levels when entering menopause. The driving force for the development of the disease is also osteoporosis, which is usually found in women at the onset of menopause.
The formulation of treatment measures takes into account the clinical conditions of the pathology. Severe symptoms do not appear immediately, and it usually takes a long time to suspect the existence of the disease. Specifically, when the symptoms become obvious, the diagnosis can already be established in the process of clearing the picture. When it comes to an obvious period, two types of symptoms should be distinguished here:
- Pain development. . . Here, we are talking about the occurrence of pain that radiates to the solar plexus area in the thoracic spine area, between the shoulder blades. Pain syndrome can migrate to the neck area, mimicking cervical osteochondrosis and enter the arm. Women often observe breast pain, which confuses them with breast lesions. Usually, pain sensations are not permanent, they are painful, but at the same time they have no intensity.
- Blood pressure disorder. . . In women with breast osteochondrosis, hypertension syndrome occurs, which is characterized by increased pressure, which can cause hypertensive crisis. A distinctive feature of normal hypertension may be that the use of blood pressure lowering drugs has little effect. If you have encountered a similar situation, you should also consult a chiropractor.
In addition to the above, other signs of thoracic degenerative dystrophy should also be distinguished:
- Pain on the left side of the chest,Not related to heart damage. . . In medical terms, this phenomenon is called heartache. Diagnosing it is not difficult, because as this symptom develops, it cannot be stopped by the use of heart medications.
- Digestive system dysfunction. . . Usually, as osteochondrosis progresses, the problem starts in the internal organs, more commonly the gastrointestinal tract. The most notable examples are the formation of heartburn, increased acidity, and a constant feeling of bloating (flatulence). Among other things, there may be problems with food digestion-nausea, heaviness, bloating after eating. In all the above contexts, the work of the chair is also disrupted-often constipation or diarrhea.
- Respiratory diseases. . . Since the malnutrition process occurs in the chest area, it is not uncommon to infringe on the respiratory system. All of these are accompanied by unreasonable dizziness, general weakness, shortness of breath and other signs that may indirectly resemble heart disease or pressure problems (artery/intracranial).
Regarding treatment, it largely depends on the signs of the pathological process. To relieve pain, doctors will prescribe painkillers, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments or gels. During exacerbations, muscle relaxants are more effective. They can reduce smooth muscle spasms, relax muscles, and relieve pain syndromes. Comments on their use are positive. When the pain becomes completely unbearable, use analgesics to block it.
Chest treatment
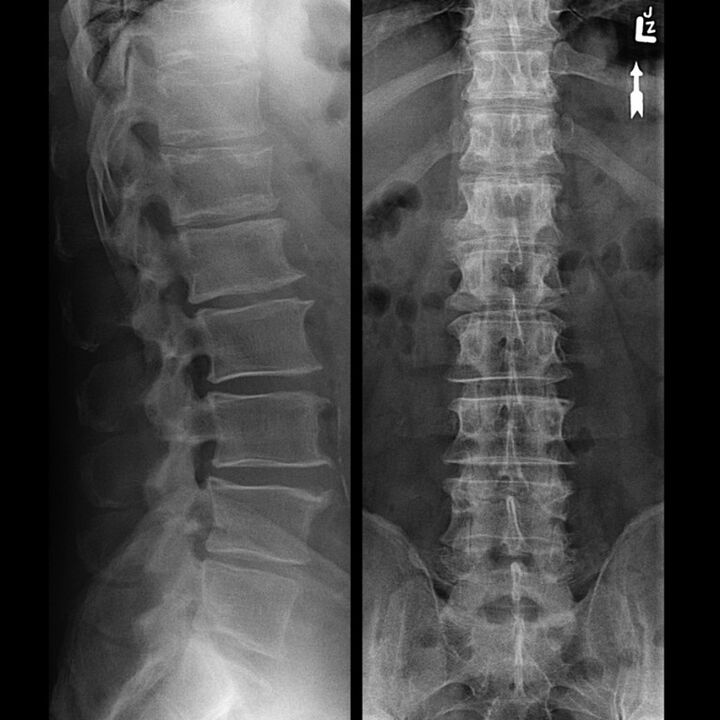
The specific manifestations of GO depend on the pathological changes that occur in the intervertebral disc. Four stages of the course of thoracic degenerative dystrophy are usually distinguished:
- Firstly. . . The symptoms are not particularly obvious, but the dehydration process of the thoracic intervertebral disc has already begun. As a result, they lose their elasticity and begin to become flatter, but at the same time, they can still withstand a certain load. Occasionally, the painful sensation of the pain type is disturbed, but it is not mild, and it is usually not necessary to take analgesics.
- second. . . At this stage, negative changes affect the annulus and various types of damage-cracks, loss of stability are observed. There are some changes in the pain syndrome, it becomes more invasive, tactile, and intensified with increased motor activity-bending, turning.
- third. . . On the X-ray, the rupture of the annulus is clearly visible, and a hernia begins to form. The pain becomes clearer, and it can flow from a complaining character to a sharper character, aggravating with exercise or even rest.
- fourth. . . Against the background of convergence of vertebrae and removal of intervertebral discs, spondyloarthropathy is actively developing. As a result, the connective tissue of the annulus fibrosus is replaced by bone tissue, which significantly limits exercise capacity.
The clinical manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis make the diagnosis of this disease more likely:
- pain. . . Almost always, it is positioned in a specific place, usually on the left. After a period of time, it will spread to the entire chest area, breathing becomes difficult, climbing stairs or exercise becomes difficult.
- Increased pain. . . Strengthening occurs when turning or tilting. Generally speaking, the same is observed when trying to breathe deeply during any physical activity.
- Muscle cramps. . . Muscle cramps plus the above symptoms, the contraction mainly falls on the upper back. In more rare cases, this symptom appears in the waist.
In addition, it is worth noting that intercostal neuralgia, which often lasts for several weeks and then disappears on its own. During this period, a person will have chest discomfort, which will aggravate during exercise, and will feel discomfort when trying to breathe deeply. Women may feel that there is a problem with the breast, which makes them consider treatment, while men may feel that there is a foreign body behind the breastbone.
It should also be noted that the above-mentioned overall clinical situation will aggravate at night or after hypothermia. The next morning, it usually becomes easier, but in the evening, everything will be repeated again.
How to treat, what methods are there, and what measures are taken? Regarding treatment measures, they should start as soon as possible. Usually, in the initial stage, it is not even possible to use drugs, but only through conventional gymnastics-exercise therapy.
The later stages of pathological development, at 2 degrees, involve the use of drugs. This includes various drug groups, and the most popular drugs are listed in the table below.
| Drug group | The main effect of the drug |
|---|---|
| Analgesics, analgesics | They relieve the pain syndrome and reduce its performance. |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) | Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and swelling. |
| Chondroprotective agent | They increase the production of secretions in the joints, slow down the process of cartilage destruction, and reduce the performance of the inflammatory process. |
| Muscle relaxants | They reduce the tension of skeletal muscles, have a relaxing effect, and help effectively cope with back pain. |
| Sedatives, tranquilizers | For more effective treatment, severe pain will cause stress, which will worsen the treatment effect. |
In addition to essential medicines, it is also recommended to take a course of medicine-vitamins.
When the overall clinical situation deteriorates, the main goal of treatment will be to relieve symptoms. In order to have a more pronounced and faster effect, analgesics are prescribed in the form of injections and steroid types.
After the exacerbation is eliminated and a stable state is reached, basic treatment must be started. A wide range of drugs can be prescribed because only a complex effect on the disease can produce positive results.
The table above describes the main drugs and then introduces them in more detail. Therefore, basic treatment will include appointments for such drugs:
- Cartilage protective agent.They are used in the form of tablets and are used for topical treatment in the form of ointments or gels. It is impossible to rule out the use of such drugs, they are the basis for complete treatment. Their role is to inhibit the destruction process of cartilage tissue and the further progress of malnutrition changes. In addition, they also increase the regenerative capacity of cartilage. However, relying on such drugs, it is impossible to completely get rid of pathology and should not be regarded as a panacea.
- Vasodilators. . . They are necessary to improve blood circulation and nutrition in the corresponding area. In most cases, doctors will prescribe a fairly effective drug to improve blood microcirculation and help relieve pain during rest.
- Local treatment. . . For best results, ointment or gel is recommended. Therefore, good results can only be achieved with the help of complex effects. Therefore, when prescribing NSAID and chondroprotective agents, ointments of the same pharmacological group are usually additionally recommended. Equally popular are creams based on bee or snake venom, which have a significant analgesic effect and are a good supplement to the main treatment.
- Vitamins. . . especially the prescription for group B vitamins. They have analgesic effects and help cope with inflammatory processes and violations of nerve endings.
- There is no doubt that with the action of drugs, physiotherapy, therapeutic massage, and exercise therapy are prescribed.
What other treatment methods should be included in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis? Experienced professionals will strongly recommend the following techniques:
- Magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, therapeutic mud;
- Complex physical therapy exercises;
- Acupuncture, Shiatsu.
It is also recommended to stick to a certain diet, exclude the use of alcohol and spicy food, and reduce the use of salt.
Special attention should be paid to therapeutic exercises, which should be performed every day, preferably several times a day. Please note that this set of exercises is individually formulated by the attending doctor (orthopedician or traumatologist). Physical education classes are carried out without deterioration. When there is no obvious pain, in the case of acute pain syndrome, it is necessary to insist on maximum rest.
Exercise with osteochondrosis is not the last thing. For this pathology, it is important to perform all prescribed exercises on a regular basis to strengthen the muscles and have a positive effect on the outcome of the treatment.
We should also mention traditional medicine. On the Internet, you can find many recipes based on natural ingredients. Folk remedies are not recommended as a stand-alone method for ecstasy, because their effectiveness will be minimal, in many cases zero. However, as an adjunct to mainstream therapy, folk remedies may be recommended. The following homemade recipes are known:
- The first ingredient: 3 tablespoons of rye flour, 1 tablespoon of turpentine and 1 teaspoon of iodine and garlic. Mix everything thoroughly and use it as an ointment at night.
- The second type: 5 tablets of Analgin sodium and 5 ml of camphor alcohol. Make the tablets into a powder state, then pour in alcohol and leave it in the form of an application overnight.
Needle applicators are considered another alternative therapy. Its effect is to relieve pain syndrome through needle massage.
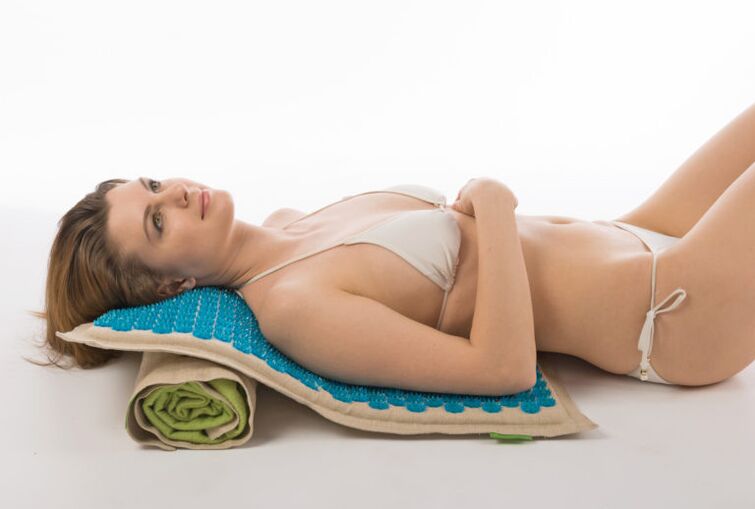

If all the described treatments do not give the expected results or the results are not durable, then decide on the issue of prescribing surgery. When the pain syndrome cannot be eliminated, surgery is necessary, and the degenerative malnutrition process continues to develop while observing negative changes in internal organ function. If the doctor still recommends that you undergo surgery, then you should not refuse it immediately. Timely intervention can allow you to get rid of such problems, fully restore the work of the organs, and rule out the further development of complications.
Surgery usually consists of two stages. The first one aims to eliminate the cause-decompression, thereby eliminating the pain syndrome. The second stage is the subsequent stabilization of the spine.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a serious disease that not only destroys the work of the musculoskeletal system, but also negatively affects the system and organs.
The important thing is to monitor your health, take preventive measures, monitor your diet and pay attention to physical activity. Regular exercise is an effective way to prevent osteochondrosis, but don't forget that any load should be moderate.
Treatment of cervico-thoracic type
Osteochondrosis in the cervical thoracic area is not considered to be an independent pathology. In this case, we are talking about a group of diseases that appear in the intervertebral discs, which can affect muscle tissue and nearby organs.
Cervical thoracic osteochondrosis is not uncommon, and more than 20% of diagnoses are attributed to this disease. This disease is very insidious. In many cases, the diversity of clinical manifestations makes doctors suspect other diseases that have nothing to do with the spine. For example, a doctor may suggest that there is angina pectoris and recommend taking medication, but it will not produce any results in the end. Worst of all, it will have a negative impact on the state of the heart system. Therefore, it is very important to distinguish osteochondrosis from lesions of internal organs. Therefore, for diseases of dystrophy in the cervical and thoracic area, the following signs are characteristic:
- Frequent headaches;
- Lose strength, then dizzy;
- Neck soreness, flowing into the shoulders, scapula, and muscle stiffness;
- Compression of intercostal nerve roots, leading to pain syndrome and its deterioration;
- Violation of blood pressure, which may drop from high blood pressure to low blood pressure, is more common in women;
- Reduced vision, hearing aid problems (hearing loss);
- In men, the effectiveness of nerve overload is reduced in the context of disease.
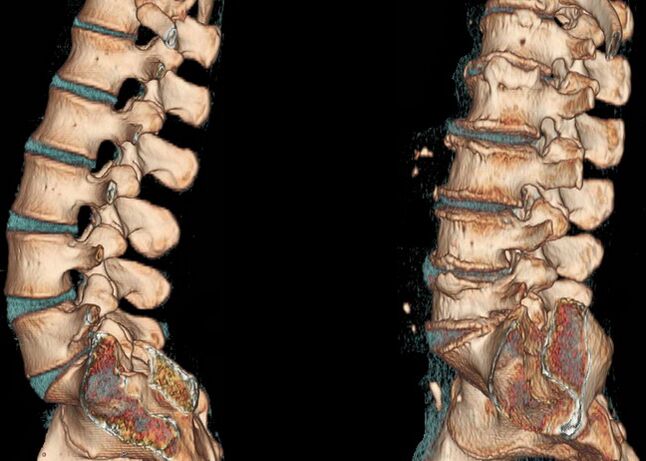
The important point is to make a correct diagnosis; many diagnostic measures will be required here, including: X-ray examination, ultrasound, MRI, CT.
Comprehensive treatment is mandatory and should include:
- drug;
- Various physiotherapy techniques;
- physiotherapy;
- Non-traditional therapy (shiatsu, acupuncture).
It is also important to take non-pharmacological measures, such as reducing physical activity, including minimizing load, changing mattresses, and buying orthopedic pillows.
Atypical symptoms, sensations, and pain
In addition to the typical pain of chest osteochondrosis, there are many atypical pains that are not related to spinal diseases. However, you should be aware of them:
- Heartache. . . Usually, in this pathological situation, heart pain will occur and mimic a heart attack at the same time. A distinguishing feature is their duration. Unlike real heart pain, the pain of osteochondrosis can last a long time, possibly for several weeks. In addition, the use of traditional medicine does not reduce the manifestations of pain. It is here that it is worth considering the existence of another pathology that has nothing to do with the heart.
- ImitationPathology of the breast. . . This clinical picture is directly applicable to the patient. Usually, thoracic osteochondrosis reminds people of breast disease, because women can observe pain in the chest area for a long time and spread to the glands. Determining the true cause of this symptom, or at least excluding breast problems, is only possible after being checked by a mammologist.
- Abdominal pain. . . This symptom makes people suspect that gastritis and other digestive diseases exist. Wrongly, a gastroenterologist can diagnose pancreatitis or cholecystitis. With the help of a thorough examination, such diagnoses can be refuted or confirmed.
- In addition to these signs, the patient may feel obviousChest discomfortDescribed as having a foreign body. It is often difficult to breathe or exhale deeply, feeling unable to breathe deeply, and shortness of breath with little physical activity.
The process of treating degenerative malnutrition is not easy, it takes a long time, the effort of the patient and the qualification of the attending physician.
Before treating the disease, be sure to consult your doctor. This will help to consider individual tolerability, confirm the diagnosis, ensure that the treatment is correct, and rule out negative drug interactions. If you use a prescription without consulting a doctor, you are entirely at your own risk. All information is for reference only, not medical assistance. All responsibility for the application shall be borne by you.