When a person has pain in a particular joint and the exact location of the pain can be pointed out, joint problems usually occur locally. But sometimes joint pain cannot be located because all joints or multiple joints are injured at the same time. It is too early to talk about rheumatoid arthritis in this case, because in addition to this pathology, there are other diseases that cover pain in all joints of the musculoskeletal system.
A careful doctor will analyze the patient’s main complaint and determine the causal relationship, which can determine the cause of all joint injuries at the same time. Determining the diagnosis is not always easy, and because of the most common general symptoms, it is impossible to select a specific pathology immediately after a series of examinations. Therefore, if systemic joint pain occurs, please do not delay medical treatment.
If all joints of the musculoskeletal system suffer from serious diseases, the following reasons may be possible:
- Pathology of autoimmune origin and systemic allergic reactions.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Chronic fatigue, increase physical activity.
- Poisoned body.
- Blood diseases.
When pain occurs in multiple or all joints, it must be remembered immediately that this condition is only a response to certain diseases, not to independent diseases. The only exception can be pathologies such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and the direct cause is damage to the cartilage itself.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
This disease refers to a chronic autoimmune disease in which the joints of the entire body are mainly affected. The distinguishing feature of rheumatoid arthritis is that many joints are involved in the pathological process.
At the same time, cytokines, metalloproteinases and chemotactic cytokines play a key role in the inflammation process. These are anti-inflammatory ingredients that can activate the body's own immune cells. As a result, they move to the site of inflammation, namely the joints of the human body, and cause a typical inflammatory response.
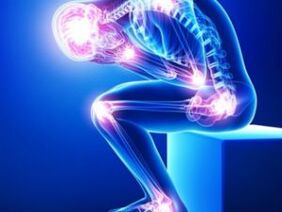
The typical manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis is damage to the surrounding joints and is symmetrical. When the disease worsens, the pathology affects the larger joints. Pathology mainly affects women, while in men, the incidence of pathology is three times less. It is diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 50, but it can sometimes occur in teenagers-this disease is called juvenile arthritis.
Although scientists have elucidated the immune properties of the disease, it has not been possible to determine the exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis-why anti-inflammatory cells acquire this pathological activity. So far, the genetic susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis has been demonstrated, and it has also been shown that negative factors such as smoking and the spread of viral diseases affect the appearance of pathology.
The course of the disease is due to the activation of immune complexes, which are produced by the synovium and found in blood vessels. The quick response to them is rheumatoid factor-antibodies produced by these complexes. In some cases, they appeared independently, without factors that caused provocation.
Help!In the early stages of pathological development, macrophages will migrate to the affected area after the number of affected lymphocytes increases. The release of inflammatory mediators stimulates the pathological process of the entire human body.
If chronic disease of the synovium occurs, its surface will no longer be its usual thickness but will become denser and thicker, growing and folding in the form of villi. Synovial fluid cells produce hemolysin and collagenase, which contribute to the destructive process of cartilage tissue. The production of prostaglandin enhances the inflammatory process, and the process of fibrin deposition and necrosis occurs.
Overgrowth of synovial tissue causes inflammatory mediators, which not only destroy cartilage but also bone tissue, ligaments and joint capsules. In the joint fluid itself, the number of white blood cells increases.
When the shape of the joint changes and the appearance becomes unsightly, the small joints of the body will be covered by rheumatoid nodules. The contents of this rheumatoid nodule are the necrotic parts of macrophages, fibroblasts and plasma cells. Similar nodules can be found in internal organs.
The disease progresses gradually. The patient suffers from general and local joint manifestations-characteristic stiffness in the joints in the morning, fatigue, loss of appetite, and body temperature rising to low fever are observed. About an hour after waking up, the condition of the joints will be much better. The joints are affected symmetrically, usually rheumatoid arthritis affects the following joints:
- wrist.
- The second and third palm fingers.
- Shoulder.
- The knee.
- Ankle.
- Buttocks.
- The elbow.
In fact, this disease threatens any joint of the musculoskeletal system. The distal phalanx joints and axial bones have the fewest elements.
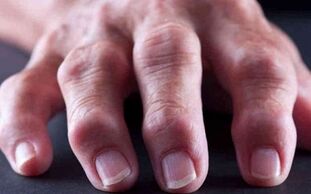
The joints are still sore, swollen and red, and they feel hot to the touch. In order to minimize pain, patients try to keep the joints bent-this will reduce the pain. The progression of the disease occurs in the first 5-6 years after the first pathological change occurs. The pathology has been developing for ten years, and irreversible changes have appeared in patients.
During this period, patients will experience significant joint deformities and may become unstable. When the nerve branches are compressed, the patient will suffer from carpal tunnel syndrome and knee rheumatoid arthritis. The patient will be threatened by Baker's cyst, deep vein thrombosis, etc.
Simultaneously with the changes in the joints, the extra-articular manifestations of the body are observed, which develop with the pathological progress of every three patients. An example of this manifestation is rheumatoid nodules in the lungs, vasculitis, Fischer syndrome, and myocarditis.
Diagnosing the disease is not that difficult. The typical clinical standard of rheumatoid arthritis was proved in the blood, the red blood cell sedimentation rate increased, and a large amount of C-reactive protein and rheumatoid factor were found.
In the case of suspected rheumatoid arthritis, the health status of the patient will be specified on the X-ray image. The disease is different from osteoarthritis, sarcoidosis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, which develops in the context of hepatitis C.
Important!When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to consider that the disease is quite lethal, but in rheumatoid arthritis, it has nothing to do with joint damage, but is related to pathological changes of the heart and internal bleeding.
The treatment of this disease is carried out through supportive therapy and powerful NSAIDs. It is recommended to apply sufficient load only on the joints and add exercise therapy. Surgery if necessary.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is another common pathology that can affect both large and small joints. Various factors can cause osteoarthritis, which firstly has a negative impact on the cartilage tissue of the joints. The cartilage of the entire human body performs multiple functions and mainly acts as a shock absorber during various exercises. Constant pressure causes increased cartilage wear.
If people with good health and strong immunity have the opportunity to restore damaged tissues, in elderly patients and patients with increased joint pressure, there will be almost no synthesis of new fibers, and cartilage tissue cannot be recovered. Traditionally, osteoarthritis was thought to be the result of mechanical action on tissues, but now doctors consider previously metastatic inflammatory diseases as factors in the development of systemic osteoarthritis.
The typical symptom of the disease is pain in all joints, because the matrix loses extremely important substances-glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. The lack of these elements leads to so-called joint dislocation, that is, cracks of various depths appear in the cartilage tissue.
Menopausal women are most susceptible to osteoarthritis.
Since the true cause of osteoarthritis has not yet been clarified, doctors have identified several factors that lead to the development of the disease:
- Congenital cartilage tissue insufficiency, it is easy to be injured. For example, patients with this pathology will have flat feet and are often diagnosed as dislocations-complete and incomplete. Gender is also one of the factors in the development of the disease, because according to statistics, the incidence of osteoarthritis in women is twice that of men.
- Age characteristics-The disease usually develops in patients over forty-five years old, and in women it coincides with menopause.
- Obesity.
- Metabolism problems.
- Increased joint exercise load.
- Traumatic joint injury.
Disease can occur in any joint, but usually the starting joint is the joint with the most physical activity. It can be positioned on the knee joint, hip, elbow, etc.
The symptoms of the disease are very obvious, so osteoarthritis cannot be missed. In a person, when the load increases, the joints begin to hurt immediately, and the intensity of the discomfort may vary: from the slight complaint in the joint to the strongest pain in the joint. When you exercise, the pain gets worse, and when you are still, the pain becomes less obvious.
Parallel to soreness, the patient will have the appearance of cracked joints and stiffness. The patient has restricted movement. Especially at the moment of disease development, when reflex muscle spasm is added to the pathological process.
In the later stages of the disease, the patient will experience characteristic joint blockage-when the joints suddenly stop moving due to severe pain, this is a severe pain. This is because fragments of cartilage tissue enter the cavity and prevent movement. If the disease is accompanied by inflammation, the synovium will swell and it is easy to observe.
The development of osteoarthritis is very individual. In some patients, X-rays show signs of pathological progression, but the perception of the disease does not change. At the same time, according to the stage of pathological development, when the joints in the picture themselves look satisfactory, other patients will feel severe pain, inflammation and restricted movement.
The diagnosis of the disease is based on X-ray data and the clinical signs of the disease. At the same time, if you need to assess whether there are complications, ultrasound scans or magnetic resonance imaging can be performed.
Doctors try to treat the disease while preserving joint mobility and the patient’s ability to work professionally. Therefore, in treatment, it is extremely important to stop the progression of the disease, eliminate joint pain and relieve inflammation.
At present, the possibilities of treating osteoarthritis are not unlimited, and because the joints cannot be restored, it is difficult to consider the treatment strategy as a success. The disease has entered the chronic stage, and you need to constantly fight against it.
Hint!However, such unpleasant predictions do not make the patient look at disability-successful treatment can enable you to learn to live with osteoarthritis and even maintain physical activity.
For treatment, the doctor used the following sets of funds:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Cartilage protector.
- means to activate blood circulation.
- Muscle relaxants.
Disease treatment is mainly composed of drugs that can restore cartilage tissue to the greatest extent and establish metabolic processes in joints. Therefore, the main focus is on chondroprotective agents, which are used immediately after inflammation has been eliminated. Treatment with chondroprotective agents is long-term, and the best results can only be achieved when treatment is started in time.
Other diseases
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are the most common pathologies of joint pain and body pain. However, in addition to the most common cause, there are other conditions that can cause joint pain.
Joint pain may be a manifestation of leukemia.
Joint pain may be a manifestation of blood diseases. Today's blood pathology is not only the most difficult in the diagnosis of the attending doctor, but also in the treatment. Usually, they are caused by tumor factors, and the meaning of diseases to patients is completely different. Usually, all joints are damaged by leukemia (acute and chronic). At the same time, since the blood test results showed no abnormalities, the patient did not even doubt what it meant.
Joint pain is not isolated, not only the joint elements are affected, but the bones and muscles are also affected. Therefore, doctors recommend that patients suffering from long-term pain should not only consult a plastic surgeon or surgeon, but also a hematologist who may suspect a pathological condition and send it to the patient for further research.
Body poisoning is another cause of joint pain. The fact is that joints react very strongly to the entry of toxins into the body. If they start to hurt and twist joints, it may be an occupational hazard, household waste poisoning, smoking and alcoholism. The patient suffers from extremely unpleasant symptoms-all joint pain, just like having the flu, the overall condition of the body is also affected.
The diagnosis may improve the patient’s health. Perform detoxification treatment to cleanse the blood, thereby removing toxins from the joint fluid.
The most important
Pain in all joints of the body is not always related to the pathology of the joints themselves. If the joints of the body are affected, it is usually the cause of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Symptoms increase rapidly and the pathological process of the joints is developing.
In other cases, when joint pain is not related to joint damage, discomfort may be a manifestation of systemic diseases, such as blood leukemia, osteoporosis, body poisoning, and infection. Coping with disease is not easy, but diagnosing disease is much more difficult. Patients with joint pain should contact the clinic in time to start treatment as soon as possible.